In this technical blog, Yoshifumi Munakata outlines recent progress made by LENZO's LLM Team in getting LLM's running on CGLA.
The rise of the token-driven digital economy demands a new class of compute architecture—one capable of delivering high performance, ultra-low power consumption, and seamless scalability. At LENZO, we are developing exactly that with CGLA (Coarse-Grained Linear Array), our next-generation compute engine designed to accelerate the AI workloads that power modern applications.
Among the most important of these applications are Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Gemini, and Llama. These models define today’s AI landscape—and we are proud to share that CGLA now runs full Transformer-based inference.
Running Llama on CGLA
The LENZO LLM Team has successfully brought Llama—one of the world’s most widely adopted open-source LLM families—to run natively on our CGLA architecture.
This achievement demonstrates:
- CGLA’s compatibility with mainstream Transformer architectures
- CGLA’s ability to execute real-world, high-demand inference workloads
- A clear path toward accelerating any Llama.cpp-based model, including Llama, Qwen, DeepSeek, Gemma, and others
Whether users choose a small quantized model or a larger configuration, CGLA handles the full inference pipeline, from prompt processing to token generation.
API Access: OpenAI-Compatible Interface
To make CGLA easy for developers to use, we integrated CGLA with the server functionality of the Llama.cpp ecosystem and exposed it through an OpenAI-compatible API interface.
This means:
You can call CGLA inference using the standard OpenAI Python client.
Developers can run CGLA inference from:
- Python applications
- Web apps
- Terminal scripts
- Custom services using the OpenAI API schema
- Any tool expecting an OpenAI-style completion/chat endpoint
The experience mirrors existing LLM workflows, but the underlying computation runs entirely on CGLA.
Example: Querying Qwen 1.5B on CGLA through the API
From a browser or Python script, a user sends:
Prompt: “What is a CPU?”
Model: Qwen 1.5B (quantized)
CGLA processes the input, runs inference using the model, and returns the generated response—just like any cloud LLM, but powered by our custom hardware.
Users can freely choose any Llama.cpp-compatible model, including Llama, Gemma, DeepSeek, and others.
Performance of Transformer Inference on CGLA
Inference performance on accelerators is typically measured in:
- Input Processing Speed
- Token Generation Speed
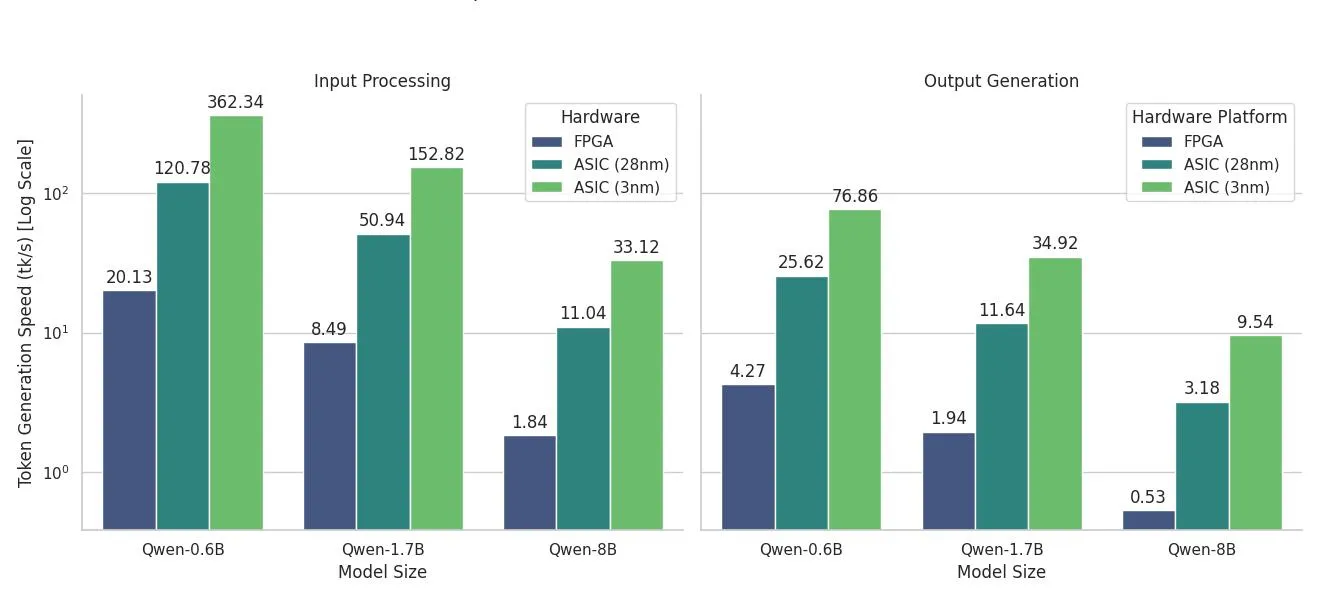
Across multiple quantized models, CGLA demonstrates strong generation performance, with projected gains as we advance toward our 28 nm and 3 nm ASIC implementations. Where CGLA truly stands out is power efficiency. Compared with an RTX 4090 GPGPU, CGLA delivers:
- Up to 44.4× improvement in PDP
- Up to 11.5× improvement in EDP
These efficiency gains directly translate to lower operating costs and more sustainable large-scale deployments.
The Road Ahead
With Llama, Qwen, and other open-source LLMs already running on CGLA and accessible through an OpenAI-compatible API, we are now focused on two goals:
1. Becoming a Hugging Face Inference Provider
Allowing anyone worldwide to run Transformer inference on CGLA instantly through the platform.
2. Achieving even higher speed and lower power consumption for CGLA-based LLM inference
Through continued architectural refinements and ASIC development.
We appreciate your support as LENZO builds the future of compute—one that is open, efficient, and optimized for the AI systems shaping the coming decade.
Thank you for following the work of the LENZO LLM Team!